Alphabetic Characters to Binary
In computers, characters are represented using a character encoding system. The most common one is ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange).
ASCII Converstion:
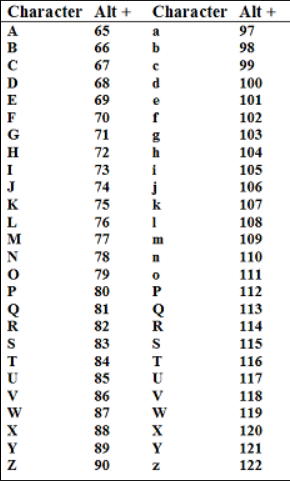
Each character in ASCII is assigned a unique numerical value. For example, the ASCII value for the letter ‘A’ is 65, ‘B’ is 66, and so on. Binary Representation:
To represent these ASCII values in binary, you need to convert the decimal (base-10) values to binary (base-2).
Binary Conversion:
Start by dividing the decimal number by 2 and note down the remainder. Continue dividing the quotient by 2 until the quotient is 0. The remainders, read in reverse order, give you the binary representation.
Let’s take the letter ‘A’ as an example. The ASCII value for ‘A’ is 65.
65 divided by 2 is 32 with a remainder of 1 (LSB).
32 divided by 2 is 16 with a remainder of 0.
16 divided by 2 is 8 with a remainder of 0.
8 divided by 2 is 4 with a remainder of 0.
4 divided by 2 is 2 with a remainder of 0.
2 divided by 2 is 1 with a remainder of 0 (MSB).
Reading the remainders in reverse order (bottom to top), we get the binary representation of ‘A’ as 1000001.